The Potential of Floating Solar PV Plants in South Africa
Over the last several years, large-scale solar PV plants have been installed to take advantage of the significant opportunity that solar power generation presents. Installations at this scale are happening internationally, regionally, as well as here in South Africa. Floating solar PV plants are a fairly new concept compared to the traditional ground-mount or roof-top solar PV plant setup. While interest and implementation of these systems are growing internationally, the local market is yet to fully tap and explore the tremendous benefits this configuration can bring.

What Is a Floating Solar PV Plant?
A floating solar PV plant, as the name suggests, consists of a PV system floating on the surface of a water body. Most of the current applications of this emerging technology have used water bodies such as dams, quarry lakes, drinking water reservoirs, canals, and ponds.
The floating plant itself consists of a floating system or pontoon, which is the underlying structure and floating system upon which PV modules are installed. There is also a mooring system which fixes the floating system to a point at the bottom of the water body or anchored to the shore to prevent free movement. As with a solar land plant, there is also the solar PV DC cabling and power conversion equipment, and finally, AC cabling for power to be transferred to land. In this case, the cable can either be an underwater cable or a floating power line. The exact setup of the plant is determined by various factors such as water level fluctuations and wind load.
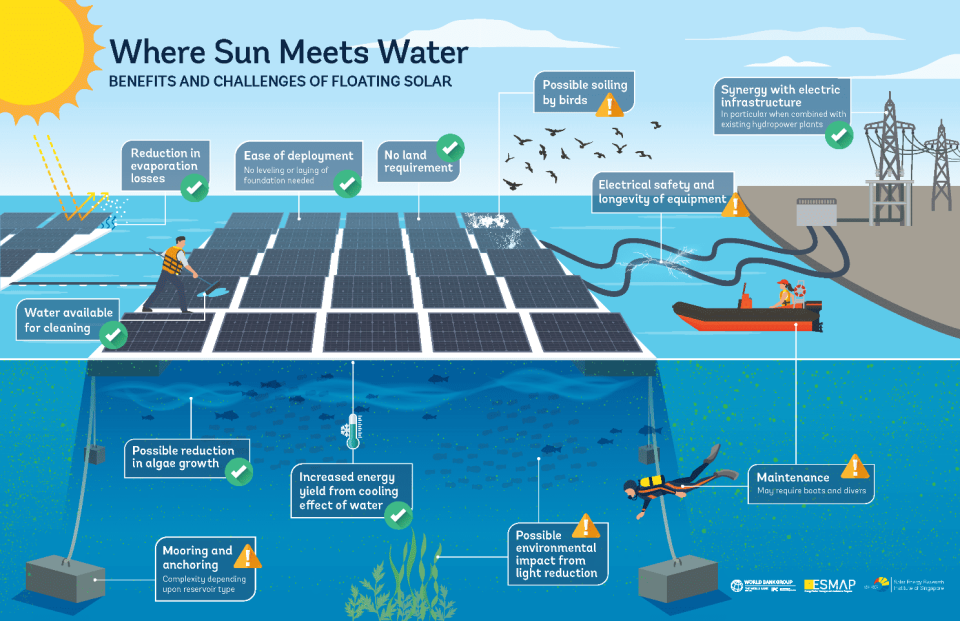
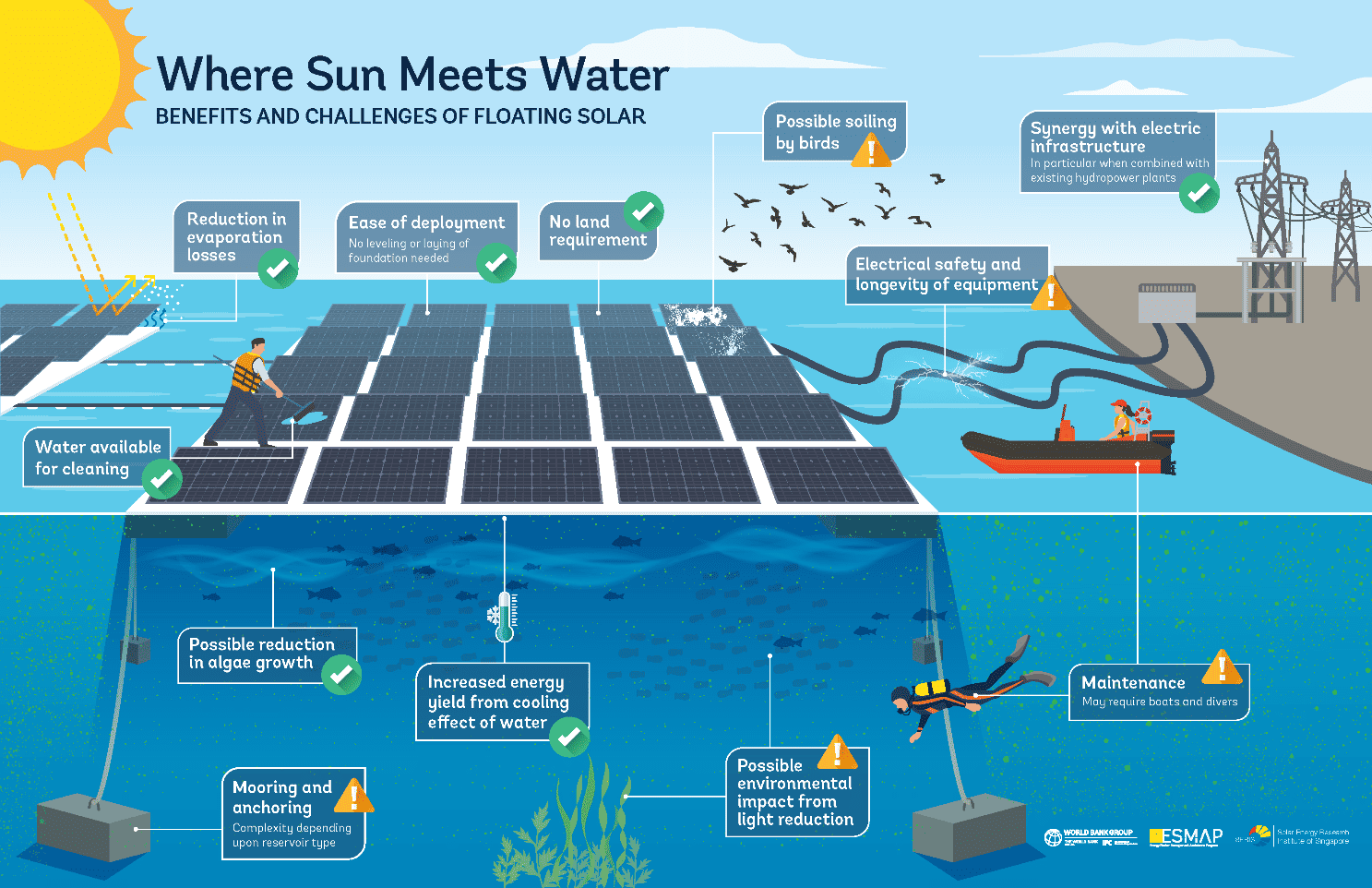
Source: ESMAP
Between 2007 and 2014, several small-scale research floating solar PV plants were built, with the first one being in Japan in 2007. In 2008, California had the first commercial floating PV plant with a 175 kWp system. Floating solar PV plants are gaining traction, with Asia leading in installations. The floating solar market has tremendous potential to double the existing installed solar PV capacity by capitalizing on 400,000 square kilometers of man-made reservoirs globally by up to 400 GW. This is according to a World Bank Report called “Where Sun meets Water.”
Because the floating power plant is still in its infancy, industry standards and best practices are still in the works. DNV GL, an international accredited registrar and classification body, is at the forefront of a floating solar joint industry project working with stakeholders to develop a best practices guide by 2021.
Advantages of Floating Solar PV Plants
Why go through all the complexities of setting up a solar power plant on water? There are numerous advantages to this emerging application. Here are the main ones:
- When existing water reservoirs are used, valuable land is freed up for other purposes such as for agricultural land or residential developments
- Setting up a floating solar plant is a much faster and easier process. The process of land acquisition for developing a plant is often prolonged and complicated. Additionally, the installation itself takes longer to deploy as geotechnical studies and foundations are required for sub-surface conditions. Not having to do a large land installation is beneficial to soil and water conservation efforts.
- A power plant on the surface of a water body results in reduced evaporation, which can be vital in areas where water is a scarce resource. This is a significant advantage to a water-scarce country like South Africa
- The combination of hydropower and solar power plants is a cost-effective strategy for allocating new PV plants. Hydropower generation is increased by reduced evaporation, which has been a major challenge in these plants. Floating solar PV can increase the capacity factor of a hydropower plant by 50- 100%.
- A floating solar power plant can generate more electricity than traditional ground-mounted and rooftop systems, about 7-14% more. This is because the water has a cooling effect, which reduces the operating temperature and increases the solar panel efficiency. Another possible contributor to the increased output is that there is less settled dust on the PV modules.
- Floating plants can improve the quality of water by creating a sunlight barrier that prevents the photosynthesis and growth of algae in water bodies.
- The cost of the solar mounting system is greatly reduced in a floating setup compared with land-based systems that require steel sub-structures and often concreted foundations.
- It is much easier to wash the plant and its components in a floating system. Additionally, the large volumes of cleaning water used in a floating are reused, leading to operational & maintenance cost savings.
- Floating PV plants are compatible with aquaculture and can be set up on an aquaculture reservoir or a fish pond, which benefits aquatic production.
- Floating PV plants are attractive and can bolster the scenery and touristic appeal of an area.
Floating solar PV plants open up a world of possibility because they can be set up on any water bodies and greatly increase the solar power generation capacity. While the advantages of the floating system are numerous, large scale rollout does present its own unique set of challenges.
Strong winds can hamper floating PV panels. The mooring system must be strong enough to resist these. Stronger supports are being developed to address this challenge. In the long-term, further research will have to be done on the ecological impact on affected water bodies. Where saltwater is used, the damage from this must be evaluated. Finally, more information must be disseminated about the installation and maintenance of floating plants as well as best practices. As mentioned, a best practice guide is already in development, which is good news for the Southern African solar PV industry in the middle to long term.
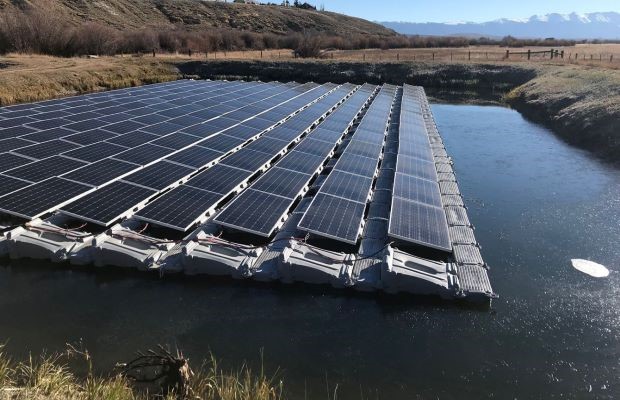

Source: Saur Energy
The Opportunity in Southern Africa
While the application of floating PV plants is fairly new, it continues to grow internationally. Many benefits can be achieved by adopting this technology in Southern Africa. In many parts of the country, water shortages and scarcity have affected normal living, especially in drought-affected areas like the Western Cape in South Africa. Floating power plants can be combined with water reservoirs to reduce evaporation losses.
Innovative solutions for the electricity generation challenges in the nation are always needed. Making using of the floating plant systems can scale up the rollout of solar PV and improve the output of hydropower stations. Floating plants are also a quicker route than the land acquisition channel, and they free up land for agriculture and other uses.
Contact Us
Contact the Zero Point Energy team to see how best we can help you make the move to reliable, renewable and self-sufficient energy.
Landline: +2710 593 4449 | Whatsapp: +27605218388 | info@enroute.xerus.co.za | TW & IG: @zeropointSA | www.zpenergy.co.za
Zero Point Energy (Pty) Ltd is a proudly South African sustainable engineering company that provides professional engineering consulting & turn-key solutions in the areas of energy efficiency, renewable energy, off-grid and energy storage solutions, water efficiency and responsible waste management. The company is a 100% black youth-owned, 30% black female-owned company achieving a Level 1 BBBEE Contributor status, and has a passion to transform the energy industry without compromising on safety, quality and client satisfaction. Learn more about the company’s team here