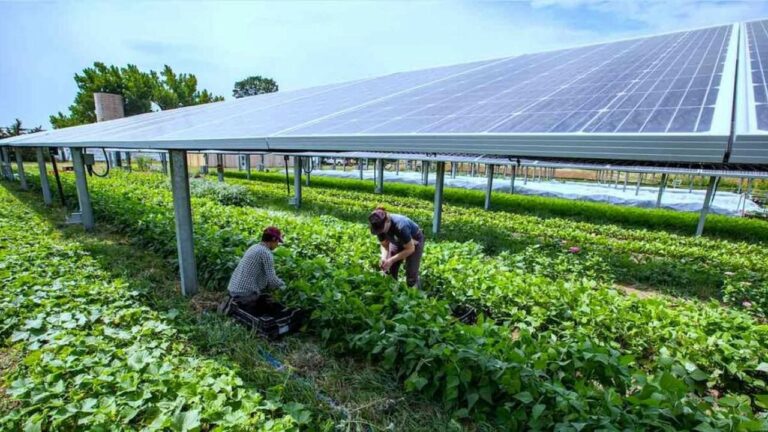
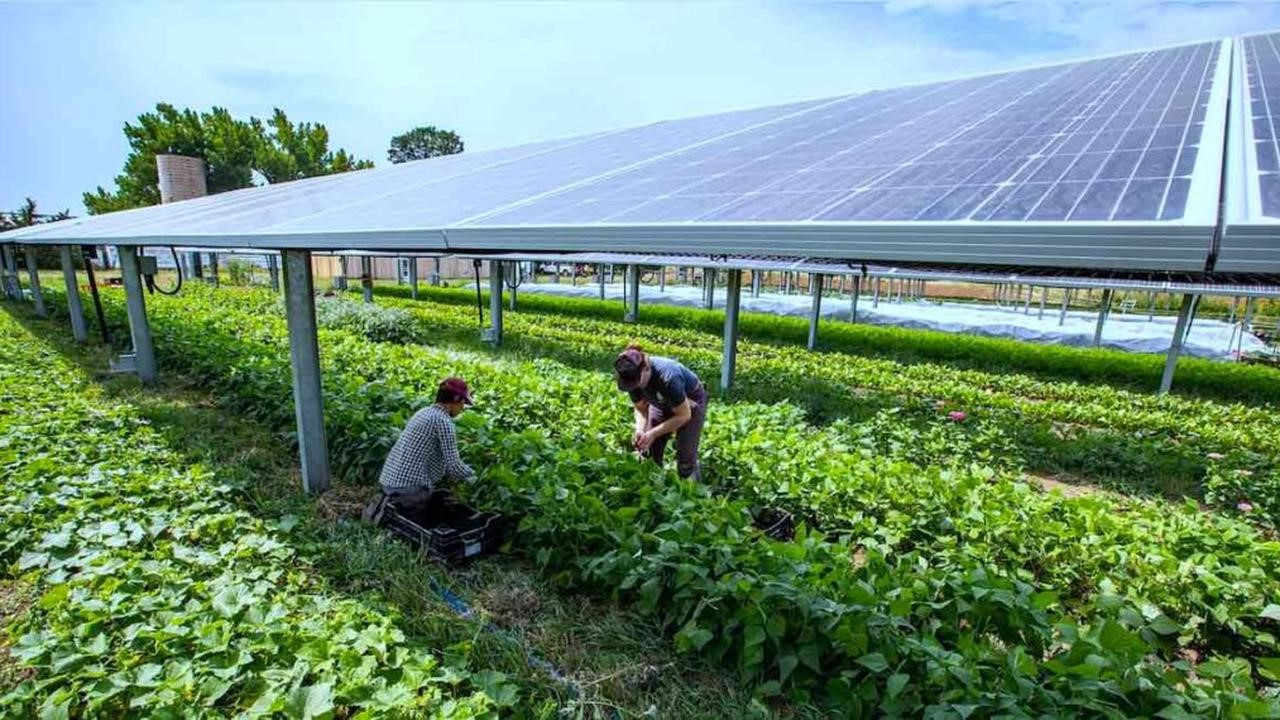
Understanding What is Solar Agrivoltaics & Applications for Southern Africa

Agriculture is a major economic activity that influences human livelihoods and the environment. Solar agrivoltaics technology leverages energy and food production in the agricultural context, producing numerous benefits. The term solar agrivoltaics may be a new one for many, but it is an exciting adaptation of technology that is yielding impressive results overseas and has great potential to make a significant impact with widespread adoption in Southern Africa. Find out more about what it is, its benefits, and usage potential locally by reading on below.

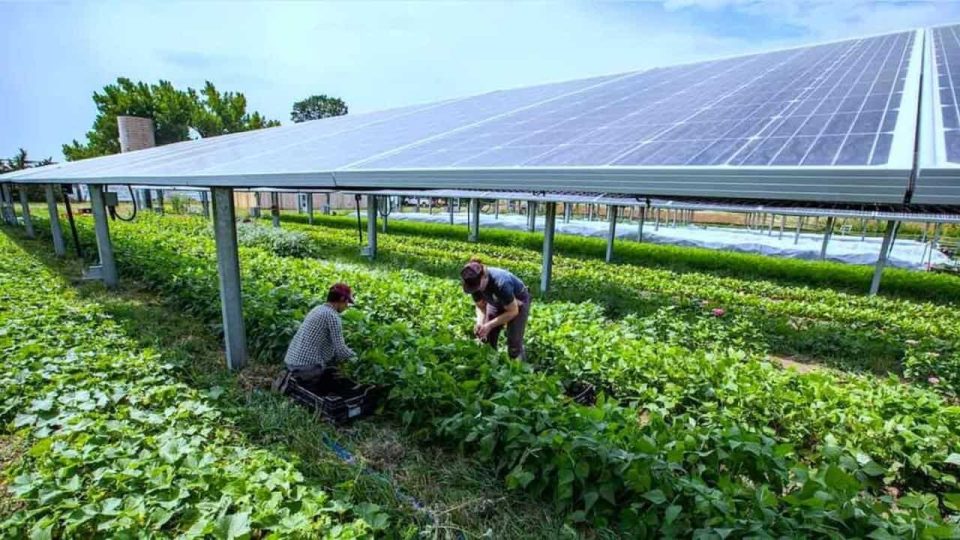
Source: Blakan Green Energy News
Background and Benefits of Solar Agrivoltaics
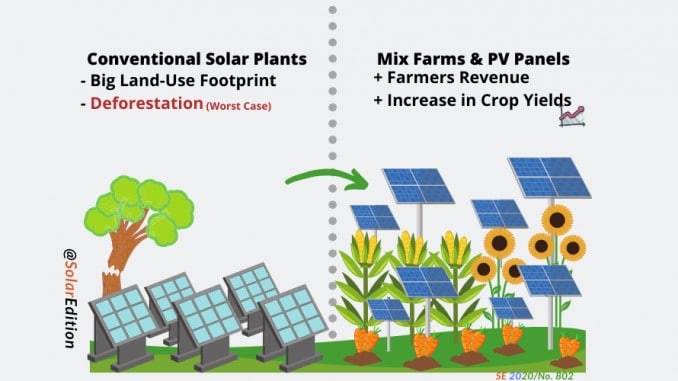
Solar agrivoltaics is a term coined by combining “agriculture” and “photovoltaics” is the positioning of solar panels directly above productive agricultural land. When this is done, the sun’s energy is used twice—to grow crops and to generate electricity through solar energy. This dual use of land reduces the large land requirements of establishing new solar farms, especially where precious agricultural land is hard to come by. Solar energy generated this way can be used to meet electricity demand on the farm for powering irrigation, refrigeration, processing equipment, and lighting, for example. This setup reduces the costs of electricity, and the surplus can even be transmitted back into the local grid and sold on to the utility company or to other offtakers.
Solar agrivoltaics is a term coined by combining “agriculture” and “photovoltaics” is the positioning of solar panels directly above productive agricultural land
Another benefit of placing solar panels on farmland is that it reduces water wastage, a major challenge in agriculture and especially important in some water-scare sub-Saharan African countries. Plants can only absorb sunlight for photosynthesis up to a certain point, which is known as the light saturation point. Thereafter, any additional sunlight increases the plants’ thirst for water and the rate of transpiration. Placing solar panels on farmland provides some shade and reduces sunlight exposure and evaporation. This in turn leads to a reduction in water demand of 20-30 %, which is a significant environmental benefit.
Having plants growing underneath the solar panels also brings about an important benefit on the solar energy production side of things. These plants have a cooling effect on the solar PV system, which is reported to lead to an increase in electricity generation on up to 10%.
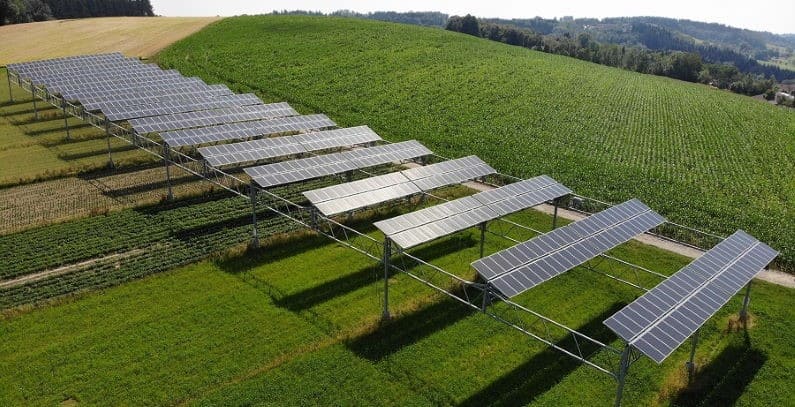
It is evident that there are many advantages of solar agrivoltaics for sustainability and for increased food and energy production. To achieve these benefits meaningfully, the design of the agrivoltaic system must be positioned strategically on the agricultural land and taking into consideration the type and nature of the crops involved. There are three typical setups, namely being interspersed between crops, raised & tilted panels, as well as greenhouse arrangements.
As far as costs, it is worth noting that the financial benefits of solar installations are paid off over time. Solar agrivoltaics may also call for longer vertical posts & and additional mounting costs associated with ensuring that wind loading and other engineering design factors are taken into consideration. It is also essential that the right type of application is selected for the right type of crops. These should typically be crops that can grow well in partially shady conditions, such as tomatoes, beans, lettuce, among many others.
Usage and Origins
Solar agrivoltaics technology is already in use in various parts of the world. It dates back to the early 1980’s when Armin Zastrow and Adolf Goetzberger pioneered the dual use of land. Since then, the technology has been further developed and widely adapted in places such as Europe, Japan, and other parts of Asia. It is also referred to as agrovoltaics, agrophotovoltaics, and solar sharing. While not yet common in Southern Africa, there is massive potential for solar agrivoltaics implementation in this region.
Potential for Use in Southern Africa
The conditions in Southern Africa are particularly suitable for the large-scale implementation of solar agrivoltaics technology. Let’s take a look at some key reasons for this:
- Availability of land- There is plenty of farmland in Southern Africa, with many different plants being grown on a large scale, thanks to the favorable climatic conditions and terrain. According to the World Bank 2018 statistics, over 75% of South Africa is farmland. Adopting solar agrivoltaics would simply mean installing solar PV on existing farmland where appropriate.
- Dual-use of land benefits- All the benefits of solar agrivoltaics can increase the efficiency and profitability of farming. Farmers can reduce their water usage and increase their local energy production. Using existing farmland reduces the need for additional land for standalone solar PV arrangements.
- Increasing electricity demand- Many nations in the region are facing increased electricity demand and challenges meeting this on a consistent basis, like the case currently in South Africa and the issues with utility provider Eskom . There is also a wide push for more renewable sources of energy. Solar energy presents a more sustainable and cheaper alternative to fossil fuel energy.
- High solar power potential- The sunny conditions in Southern Africa are ideal for generating solar energy. Solar PV installations in residential and commercial spaces are on the rise, and this can be extended to the agricultural industry as well.
- Rural electrification- Solar agrivoltaics can be implemented successfully on a small scale or on a large commercial scale. With many parts of Southern Africa still without electricity, there is potential for the technology to be rolled out in tandem with rural electrification projects.
- Reduction of evaporation in water-scarce regions- Many parts of the region are facing water shortages. This challenge is only exacerbated in the years when rainfall is particularly low. The installation of solar PV on farmland can help to reduce water usage and water losses and thereby help in the battle to conserve this precious resource.
Local Example of Solar Agrivoltaics
Locally in South Africa, the installation of solar PV on farmland accounts for only 10% of solar projects, and for the majority, this relates to installations on rooftops or on land separate from crops. Solar agrivoltaics has been introduced locally but is still gaining traction.
An excellent example of the large scale use of this technology is the Eskom pilot project at Komati power station. As part of its push to reduce fossil fuel energy production and increase renewable energy generation, the state-owned electricity utility is exploring the use of existing land at the Komati coal-fired power plant into an agrivoltaic plant, and tenders have already been issued towards this goal.

As plans are underway to shut down the coal fire station towards the end of 2022, Eskom has rolled out an elaborate plan to repurpose the Komati site under their Just Energy Transition project. The plan will involve establishing a 500-kW agrivoltaic system accompanied by a battery storage system, a microgrid assembly, as well as a fabrication factory.
With many eyes on this new development, this is a chance to demonstrate the use and value of combining solar and crop production on the same piece of land. Eskom also intends to run similar projects on other power plants set for retirement in the next few years, such as Grootvlei, Hendrina and Camden power station.
Summary & Conclusion
The adoption of solar PV has been widespread across the globe and in the region, with many possible applications. While many installations are found on rooftops or occupying uncultivated land, the dual use of land for solar energy generation and agriculture produces some significant synergies.
Solar agrivoltaics increase the efficiency of solar PV systems, thanks to the cooling effect of having plants underneath the panels. It can also improve crop production, reduce evaporation, and water usage. Such systems have been around for decades, and although common in many parts of the world, it’s time for their widespread adoption in Southern Africa. The availability of land, huge farming culture, and sunny conditions make this technology ideal to help improve solar energy production, efficiency, and water conservation and address some of the unique challenges the region faces.
Contact Zero Point Energy today to assess, design and install your next solar agrivoltaic solution:
Landline: +2710 593 4449 | Whatsapp: +27605218388 | info@enroute.xerus.co.za | TW & IG: @zeropointSA | www.zpenergy.co.za
We are also a proudly South African sustainable engineering company that provides professional engineering consulting & turn-key solutions in the areas of renewable energy, energy efficiency, energy storage & backup power. The company is a 100% black-owned, 41% black female-owned company achieving a Level 1 BBBEE Contributor status, and has a passion to transform the energy industry without compromising on safety, quality and client satisfaction. Learn more about the company’s team here
#agrivoltaics #solar #agriculture #energyefficiency #energysaving #costsaving #sustainability #greenenergy #renewableenergy #solarpower #engineering #design